KEY TAKEAWAYS - Digitization, the process of turning paper-based information into a digital format, makes research more efficient and reproducible, saving time and money. In the U.S. alone, over $28B are lost annually on research that is not reproducible. Artificial intelligence (AI) goes hand in hand with digitization in labs and comes with transformative benefits. Electronic lab notebooks (ELNs) might be useful tools for digitizing data after working in the lab, but they come with challenges at the bench. Voice technology is the key to integrating AI and digitization technologies into lab workflows.
NO PROGRESS WITHOUT DIGITIZATION
From their first day at the bench, scientists are reminded again and again that accurate documentation is the key to efficient research. Every step of an experiment must be recorded. Thorough documentation makes research more reproducible, intellectual property easier to protect and regulatory guidelines easier to meet(1,2). Digital tools can simplify the documentation process.
Lab Digitization
Digitization – the process of turning analog information into a digital format(3) – has taken over many aspects of our lives. Much of what used to be written, sketched or documented by hand, such as our medical records, bank statements, and even newspapers, has moved from a paper-based format to a paperless state(1).
In science, it is no different. All over the world, researchers are swapping their pens, paper notebooks, and sticky notes for digitization technologies, such as Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs), Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMSs), and Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), and Manufacturing Execution System (MES) software (2). And they have good reason. After all, laboratory digitization has many benefits.
BENEFITS OF LABORATORY DIGITIZATION
First and foremost, digitizing laboratory data greatly simplifies record keeping(1,2,4). Researchers can easily sort, label, store, access and search digital data. This streamlines workflows and increases productivity in the lab(2,4,5). Digital data also facilitates collaboration by allowing researchers to combine and compare datasets and share them between labs all over the world(2,4,5). And when new regulatory standards pop up or IT systems are updated, digital data allows researchers to easily update experimental setups(2). Data security is one of the greatest benefits offered by digitization. Paper-based documents are always in danger of being damaged(4). Even something as simple as a spilled cup of coffee can destroy hours of hard work. Nowadays, however, digital data can be encrypted, securely stored in clouds and protected by access control.
Moreover, digital data makes it much easier to create a full audit trail for intellectual property protection (IP) or regulatory compliance. Digital data platforms can automatically track data entries or edits with time stamps so it is very clear who contributed to new ideas and when IP was generated. This is much more difficult to validate with paper documents than with digital audit trails.
Overall, lab data digitization improves processes, simplifies workflows and makes research and development (R&D) more efficient(2,5). And with increasing advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI), digitization in the research environment is set to become an integral part of every laboratory.
MODERN DAY LABORATORY DIGITIZATION: ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Scientists working today have access to more tools and more data than ever before. However, this brings with it the challenges of analyzing big data sets and combining data from many different sources. AI and machine learning tools can help scientists integrate data and connect equipment. Although AI and machine learning are still in their infancy, these tools will become increasingly valuable in research laboratories.
Not only will AI enable communication with and between automated lab instruments, it will also have the ability to constantly learn from all information saved in a system, such as experimental protocols and data points(6,7). Language-based AI programs can also extract relevant research data from publicly- available databases, such as PubMed(7).
With access to large datasets, scientific texts, images, and videos, AI may one day be able to compare and contrast studies, making it easier for scientists to set up hypotheses and design experimental protocols or follow-up studies(2,6,7). Scientists will be able to exploit the benefits of AI to simplify their workflows and accelerate research timelines.
“Digital assistants will free employees up to
work on the things that matter most. New forms of
interactions such as voice or image recognition, in
conjunction with machine learning technology, will
push businesses further than ever before. LabTwin
has the power to accelerate communication, unleash
creativity and increase productivity by freeing
scientists from keyboards, desktops, and hard-to-
access folder structures. It’s the digital twin
always within reach.”
Magdalena Paluch
LabTwin CEO, co-founder
LAB DIGITIZATION 1.0: THE ELECTRONIC LAB NOTEBOOK
The development of the electronic lab notebook (ELN), in the early 2000s, swayed many researchers to move from a paper-based documentation system to a digitized process. For nearly two decades, ELNs have slowly been pushing analog notebooks onto the sidelines(8, 9).
ELN difficulties
ELNs allow researchers to search through data resources, archive old data, document progress, and share data with colleagues and other research groups(10,11). Moreover, ELNs can help researchers organize experimental findings, providing a clearer overview of research processes(10,11).
However, ELNs are not all they are cut out to be. Researchers often feel that importing and documenting their data via ELN can be more time consuming than original documentation methods(11). Part of the problem is caused by complicated interfaces. Researchers can have difficulties navigating ELN software(10,11). Furthermore, scientists commonly use hazardous chemicals, fragile biologicals, or sterile cultures in their experiments. ELNs cannot be used in these environments. Therefore, researchers are often forced to leave their experiments and move to their office in order to document their processes. This greatly disrupts workflows and can waste valuable time(11,12).
What if there was a way to circumvent these problems, keep the benefits of digitization, but also provide a simple, user-friendly method to document findings in any lab situation? The Berlin-based company LabTwin has the answer: a voice- powered lab assistant.
LAB DIGITIZATION 2.0: MAKING LABORATORIES PAPERLESS WITH VOICE TECHNOLOGY
As early as the 1940s, Alan Turing dreamed of developing a computer that would have the ability to communicate with people through speech(13,14). In the 1990s, this idea began to take shape and researchers started looking for situations in which human-computer communications would be advantageous: for instance, when a person is busy using their eyes or hands, or when the availability of a keyboard or screen is limited(14). In a laboratory, these situations are very common and voice assistance at the bench could revolutionize how scientific organizations and researchers work.
Voice Powered Assistant
Voice-powered assistants are already in use in healthcare settings, providing support to patients and caregivers(15). Voice assistants can remind patients to take their medication, go to appointments, or provide information about specific symptoms(15,16). In clinical trials, voice assistants can explain difficult information to patients and guide them through complex trial structures(15,16).
Although voice technologies could greatly improve documentation processes and workflows, they are still largely missing in the laboratory environment(17). With its voice-powered lab assistant, LabTwin is addressing the challenges that many researchers face when digitizing laboratory data or working with ELNs. LabTwin can guarantee a streamlined workflow, because researchers do not have to remove their gloves or otherwise interrupt their experiments to capture data points, take notes and access information(17). This makes the documentation of laboratory processes quicker, easier and more comprehensive.
“LabTwin is a research tool we all, as scientists,
can greatly benefit from. We are at an era in which
technology is at our fingertips, and having a tool
like LabTwin that allows integration of multiple
functionalities within a laboratory annotation
system greatly simplifies our research workflow.
I am convinced LabTwin will change research.”
Ernesto Diaz-Flores
Assistant Adjunct Professor at UCSF
BENEFITS OF LABTWIN
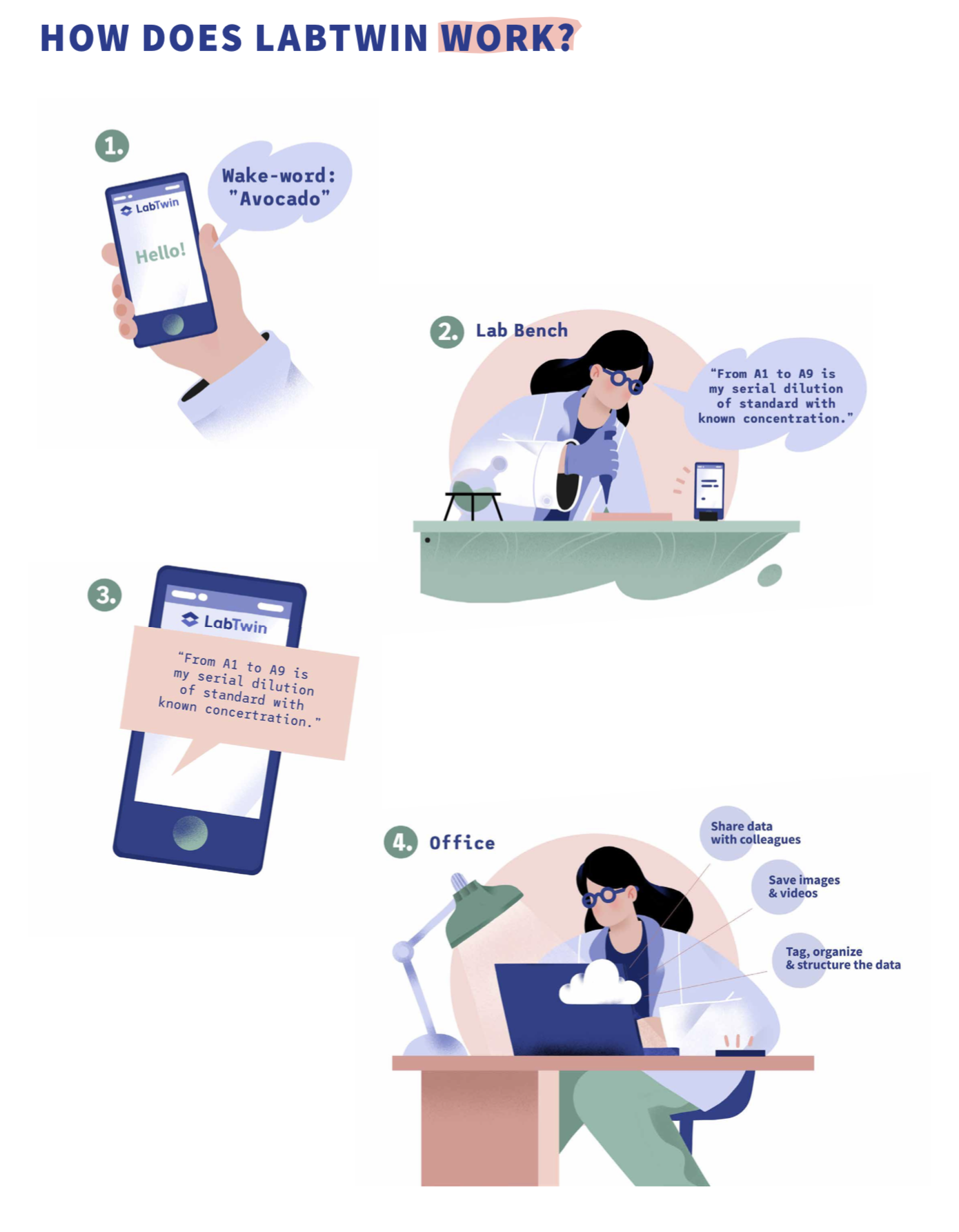
By simply talking to the LabTwin app, researchers can document every step of their work at the bench, set reminders and create entire order lists without leaving their workspace(17). Unlike other voice recognition tools on the market today, which are geared towards the consumer market, LabTwin is geared towards the scientific market(17).
LabTwin’s voice recognition software is specifically designed to understand scientific vocabulary.
For instance, it will understand the difference between a “microarray” and a “microwave”, and unlike other marketed voice recognition software, it can also understand scientific acronyms, such as “ELISA”, which it would document as the uppercase acronym, or “micrograms”, which it would write down as the unit of measurement(17).
Researchers can save experimental details immediately by directly dictating their observations, experimental conditions, data points and results to the app while they work. LabTwin then transcribes their speech into text and automatically synchronizes with the web-based app so all observations are ready and waiting when researchers get back to their computers(17).
“We realized that with all the best documentation
systems in the world, there is still a gap that
needs to be fixed between the work that is being
done and the work that needs to be documented. So
we decided to develop LabTwin to allow hands-free
recording in real time.”
John Egerton
Head of Sales at LabTwin
What is more, the LabTwin app uses artificial intelligence to learn from what researchers are telling it(17). When a researcher later corrects any voice notes taken at the bench, the LabTwin software will study these corrections and remember them for next time, becoming smarter and more in tune with an individual researcher’s workflow(17).
LabTwin allows researchers to keep all lab information – including text, images, data points, protocols and material safety data sheets – secure and safe in one place so it is easy to access, search, edit and share(17). This allows laboratories to standardize protocols, enables researchers to reproduce experiments and data, and prevents them from having to repeat experiments because data was lost or experimental conditions were not documented(17). As a result, researchers can work faster and more efficiently, leading to more reliable and therefore, more reproducible research(17).
As well as being efficient, LabTwin is also secure. The app complies with regulatory guidelines on data privacy and uses data encryption, user access tiering and private networks to protect lab data(17). The app allows labs to create a complete audit trail of their work with automatic timestamps, electronic signatures, and secure data storage(17).
THE FUTURE OF LABORATORY DIGITIZATION & ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
In recent decades, laboratories have undergone a continuous change, moving from paper-based documentation systems to paperless systems. Not only that, laboratories are also experiencing a steady evolution from electronic systems to data-driven, integrated technologies(8). In short, laboratories are becoming smarter.#
Smart Digital Labs
Smart digital laboratories are characterized by an increasing variety of software packages and management systems, which can all be linked to further technologies, such as mobile phones, clouds and the so-called Internet of Things (IoT)(8). Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning facilitate the work with large datasets and supply researchers with an accuracy that has never existed before(18).
Lab wide integration
With more and more integrative technologies available today, the key, in future, will lie in identifying those technologies that are best suited for specific laboratories and understanding how certain aspects of the lab could be improved(8). By linking all smart technologies in a digital laboratory, data could be fed directly into a smart documentation system, which would greatly lower the risk of human error and streamline workflows(8). Researchers will then be able to access their data from anywhere at any given point in time, as well as share their data with colleagues all over the world. Collaboration will drive innovation(19).
Laboratories have undergone a revolution in terms of acquiring and handling research data and information(8). The modern laboratory aims to incorporate the latest tools, software, and technologies to enhance the scientific method – which, in principle, remains unchanged and continues to focus on the development, analysis, and adjustment of hypotheses through careful and precise observation, assessment and experimentation(8). By integrating seamless systems and enabling access to large data sets, disruptive and risky paper-based processes will be eliminated once and for all(20).
ABOUT LABTWIN
LabTwin is creating the next generation of digital lab tools, starting with the world’s first voice-powered lab assistant. With LabTwin’s assistant, scientists can collect data, manage experiments and reagent inventories, and streamline documentation simply by talking. LabTwin is backed by Boston Consulting Group Digital Ventures (BCG Digital Ventures) and Sartorius. Their voice-powered assistant is used by scientists around the world.

LIST OF REFERENCES
-
Shepherd, C. 2015. The Scientific Process: Are You Ready to Digitize? Digital Science
-
Noelken, G. 2017. The Lab Digitalization Loop Picks Up Speed. Data4Lab Consulting Ltd.
-
Bloomberg, J. 2018. Digitization, Digitalization, And Digital Transformation: Confuse Them At Your Peril. Forbes Media LLC
-
Aptara Corporation. 2018. 10 Advantages of Digitization and Data Capture You Must Know. Aptara Inc.
-
Naujok, N et al. 2016. Research and Development 4.0, The Mutual Benefits of Digitization and R&D. pwc
-
Painell, L. 2018. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Instrument Automation. Laboratory Equipment
-
Gil, Y et al. 2014. Amplify Scientific Discovery with Artificial Intelligence. Science, 346(6206):171-172
-
Boogaard, P et al. 2018. Building a Smart Laboratory 2018. Scientific Computing
-
Machina, HK & Wild, DJ. 2013. Electronic Laboratory Notebooks Progress and Challenges in Implementation. Journal of Laboratory Automation, 18(4):264-268
-
Dirnagl,U&Przesdzing,I.2016.APocketGuidetoElectronicLaboratoryNotebooksinthe Academic Life Sciences. F1000 Research, 5(2)
-
Girdwood,D.2013.ElectronicLaboratoryNotebooks–helporhindrancetoacademicresearch? The University of Edinburgh, Research Data Blog
-
Robyr,J.2014.TheChallengesofthe(Electronic?)LabNotebook.EcolePolytechniqueFederale de Lausanne
-
Turing,AM&Bayley,D.1945-46.ReportonSpeechSecrecySystemDELILAH.Cryptologia,36:295- 340, published in 2012
-
Cohen,PR&Oviatt,SL.1995.TheRoleofVoiceInputforHuman-MachineCommunication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 92:9921-9927
-
Robinson,R.2018.Trend:VoiceAssistants.PharmaVOICE,65-70
-
INVOCA.2018.TheRiseofVoice:WhattheIncreaseinConversation,VoiceAssistantsandAIMeans for Business.
-
LabTwin. 2019. The World’s First Voice-Powered Lab Assistant.
-
Heer,J.2019.Agencyplusautomation:Designingartificialintelligenceintointeractivesystems. PNAS, 116(6):1844-1850
-
May,M.2017.Companiesinthecloud:Digitizinglaboperations.Science
-
Giles,J.2012.GoingPaperless:TheDigitalLab.Nature,481:430-431



