Pharmaceutical companies face increasing pricing pressure on new medicines, and many have turned to automation to shorten product development timelines, facilitate compliance and reduce costs. By automating repetitive manual tasks, such as pipetting, laboratories can lower error rates and increase throughput. Automation also frees scientists up to work on higher cognitive tasks like experimental design and troubleshooting.
From connected devices and automated workstations through to flexible robotic arms and collaborative robots (co-bots), lab automation has found‚ its place in pharmaceutical R&D labs.
A major advantage of lab automation is that it generates high-quality data by preventing human transcription errors or data loss while facilitating traceability, making it a powerful asset for compliance and analytics.
LAB AUTOMATION: HIGH-THROUGHPUT AND STREAMLINED COMPLIANCE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Lab Automation: High-Throughput and Streamlined Compliance
Implementation and Integration Hurdles
Digital Lab Assistants: Connecting Scientists
to the Digital Ecosystem
Case Study 1: Configuring Automated Platforms The Challenge LabTwin’s Solution
Case Study 2: Connecting Automation Islands
The Role of Digital Lab Assistants in Semi-Automated R&D Labs
IMPLEMENTATION AND INTEGRATION HURDLES
Organizations are still, however, working on maximizing the benefits of lab automation. In many labs, scientists are still responsible for integrating data from different automated platforms and surrounding manual processes. Researchers are hampered by difficulties when trying to access various informatics systems from the bench or share up-to-date documentation, such as SOPs and robot configuration settings, with colleagues.
DIGITAL LAB ASSISTANTS: CONNECTING SCIENTISTS TO THE DIGITAL ECOSYSTEM
Built to enable data capture and access at the bench, voice-powered digital lab assistants are the mobile interface between scientists and their informatics systems. Digital lab assistants permit hands-free data exchange and integration while leaving workflows uninterrupted, providing the missing link between scientists and the connected lab.
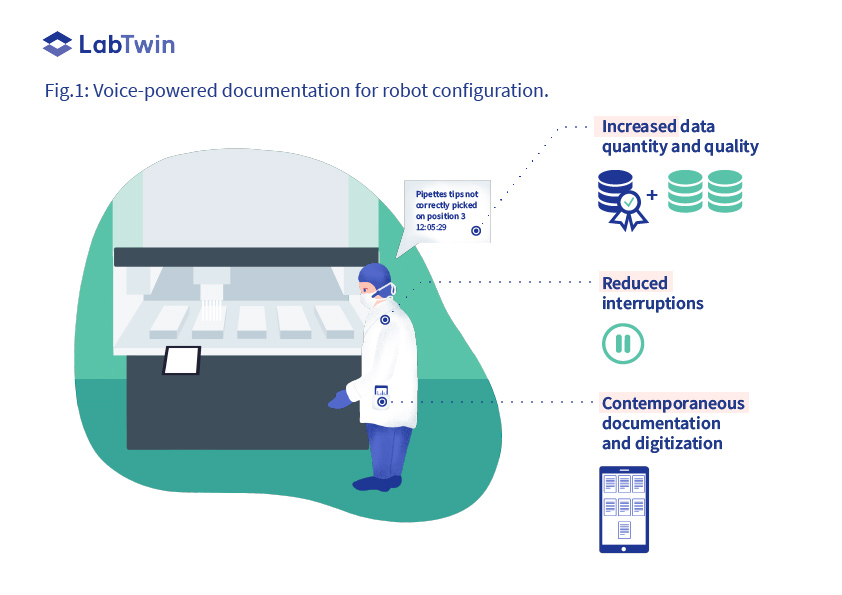
CASE STUDY 1: CONFIGURING AUTOMATED PLATFORMS
The exploratory nature of R&D requires adaptable and flexible automation. This is usually built with a series of modular and configurable platforms performing specific tasks. Custom configurations should be developed to ensure any new robotic system fits into current lab workflows. This includes finding the optimal parameters to fit the needs of scientists, updating the code accordingly and sharing the corresponding SOP with users and collaborators. Configurations usually need to be updated several times a year, always under constant time pressure to get the system back online as soon as possible.
The Challenge
Scientists or engineers in charge of configuring a robot and writing up a new SOP must run several trials and closely observe the gestures of the robot or operating scientist while recording all tested variables, results and observations. To keep up with the speed of execution, most scientists keep this information in their memory until they can write the data down at the end of the trial. Scientists often find themselves repeating trials several times to capture forgotten or missed information.
“If I take notes, I cannot keep my eyes on the robot and I miss crucial information.”
LabTwin User Associate Scientist, Pharma Company
In some labs, scientists are not allowed to use computers or paper at the bench, making the documentation process even more challenging. Documentation is either postponed or interrupting the workflow to go out of the lab. Unfortunately, both methods result in poorer documentation of the process which would likely hamper future troubleshoot- ing and reproducibility.
“I am always running from the lab with robots to my computer back in my office.”
LabTwin User Senior Automation Engineer, Top Pharma Company
LabTwin’s Solution
By enabling hands-free data capture through voice recognition, LabTwin’s voice-powered digital lab assistant allows real-time documentation without distracting scientists’ focus from their lab tasks.
“I always carry LabTwin with me. It was really helpful to work on our pipetting robot.”
LabTwin User Senior Technician, Pharma Company
With LabTwin, the quantity of data collected is higher than with traditional methods and data is automatically digitalized and structured, saving considerable post-processing time. Moreover, the digital lab assistant can take pictures of the set-up which can illustrate a new SOP more accurately.
“I use LabTwin as my third arm, recording the change I made for each tested parameter
and the reason behind it. I can then easily share the fully documented process with our
US counterparts.” LabTwin User Senior Automation Engineer, Top Pharma Company
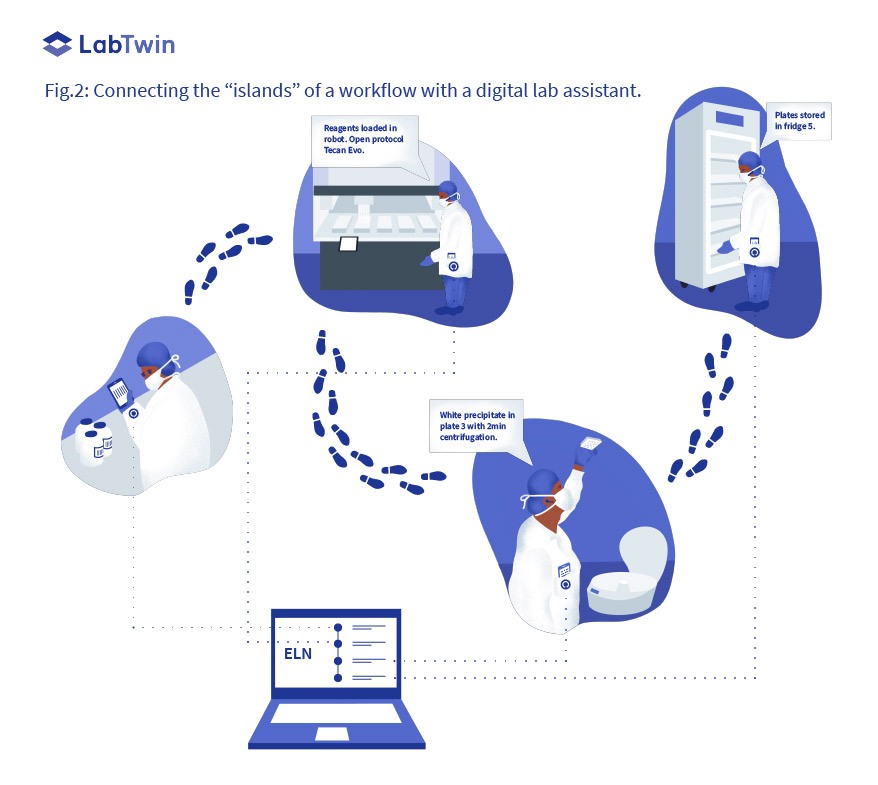
CASE STUDY 2: CONNECTING AUTOMATION ISLANDS
Compared with manufacturing, the need for flexibility in R&D labs prevents their full automation and instead, results in several isolated ‘automation islands’ only connected by scientists.
The Challenge
Significant progress has been made in building digital dataflows from automated platforms to data repositories. However, integrating data generated from different parts of a workflow and retracing the steps that led to the results remains a heavy burden involving a lot of manual data handling.
"The most tedious parts of the research involve compiling data from different places.”
LabTwin User Associate Principal Scientist, Top Pharma Company
LabTwin’s Solution
LabTwin’s protocols verbally and visually guide scientists through the manual steps of setting up as well as handling a robot which eliminates distractions, reduces human errors and ensures compliance.
“To connect those islands, you want a companion with you, with voice or AR, allowing
you to design the digital workflow in real time with flexibility.”
Andreas Steinbacher, Lead Discovery Informatics Data Management, Roche
Furthermore, as a mobile companion, LabTwin allows complete tracking of experimental context from one device to another, recording the equipment and reagents used and integrating this information with any extra observations or deviations noted during the procedure. Automatic metadata enrichment and data structuring result in improved data quality.
“Having a picture of the deck layout and labware to be used
in the protocol is very helpful.”
LabTwin User, Associate Scientist, Top Pharma Company
THE ROLE OF DIGITAL LAB ASSISTANTS IN SEMI-AUTOMATED R&D LABS
The R&D Lab of the Future is a semi-automated environment of modular hardware and mobile scientists, connected with lab software through dedicated interfaces. By being both user and data-centered, digital lab assistants are the ideal interface between scientists and the digital ecosystem, witnessing every step of a workflow and connecting the pieces together. Digital lab assistants support scientists by giving them seamless access to their digital environment. With digital assistants, labs can achieve higher data integrity by bridging the gap between automated platforms, scientists and lab informatics systems.