Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) regulations require that companies maintain minimum standards for processes, equipment, facilities and quality management systems. However, it can be challenging to accurately record and track various data streams in real time, within manufacturing facilities. Voice-powered digital lab assistants can provide a solution to this problem by directly communicating with lab instruments and automatically transcribing voice notes from staff. They are the laboratory equivalent to personal digital assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa, the Google Assistant or Apple’s Siri. While the integration of voice assistants into daily tasks has become a growing trend in the consumer market, the technology has yet to be implemented widely in laboratory and manufacturing environments.
Yet there is great potential for digital lab assistants to improve the quality and efficiency of both research and development (R&D) and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Digital assistants ensure collection of complete, accurate and contemporaneous data that can be easily attributed to staff members via user identification, automatic timestamps and electronic signatures. LabTwin has developed the first voice- and AI-powered digital lab assistant which can bring the advantages of voice assistant technology to the pharmaceutical and allied industries.
A panel of industry experts recently gathered in a round-table style webinar to discuss the importance and challenges of data integrity in a GMP environment, the methods by which digital lab assistants maintain data integrity, security and auditability and how digital tools can facilitate real-time data-driven decisions and improve quality management.
Data integrity
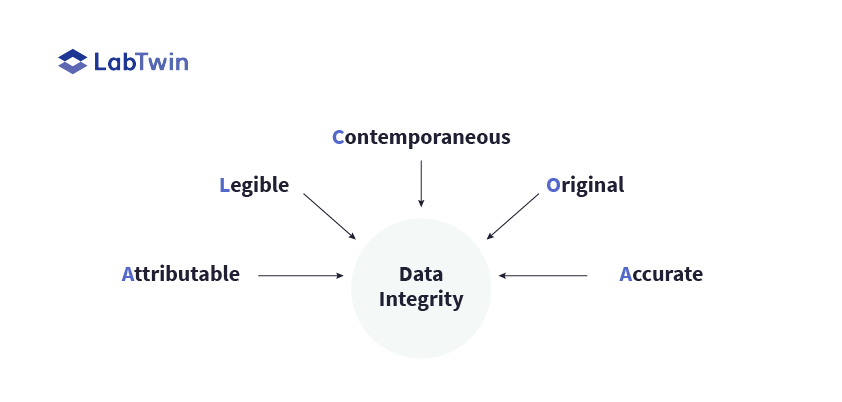
Data integrity is of paramount importance in the pharmaceutical industry. It is the Federal Drug Administration’s (FDA) highest priority during site inspections and in fact, spans many other industries aside from pharmaceuticals. The term ‘data integrity’ refers to the extent to which all data is complete, constant and accurate throughout its lifecycle. This spans initial data generation through processing and transformation of the data, as well as data transfer from manual to computerized systems. Once in the computerized system, the remaining lifecycle involves data retention, archiving, retrieval and finally, data destruction.
To learn more about data integrity in the pharmaceutical industry, visit LabTwin’s webinar recording on the topic.
“A core principle of data integrity is that the data must be recorded at the time when it was generated. Data must also be accurate and correctly reflect experimental observations.”
Steffen Gloth
Co-founder and Head of Operations, LabTwin
Data management and cGMP
A major challenge with cGMP data management is the digitization of data that have been recorded manually in a laboratory notebook or other paper methods. Digitizing data often means creating a system that is a hybrid of paper systems and electronic systems, such as a manufacturing execution system (MES) or laboratory information management systems (LIMS).
Digital lab assistants provide automatic data digitization at the bench, ensuring data is original, accurate, contemporaneous and enduring. Voice assistants also improve data traceability, an essential part of regulatory compliance. For example, in pharmaceutical manufacturing, records must be maintained for seven years past the exhaustion of a product batch.
“How do you get those two things to connect with each other in a way that you’re maintaining originality?”Cheryl Blasie
Director of Analytical Quality & Compliance, Bristol-Myers Squibb
Digital lab assistants and their applications to cGMP
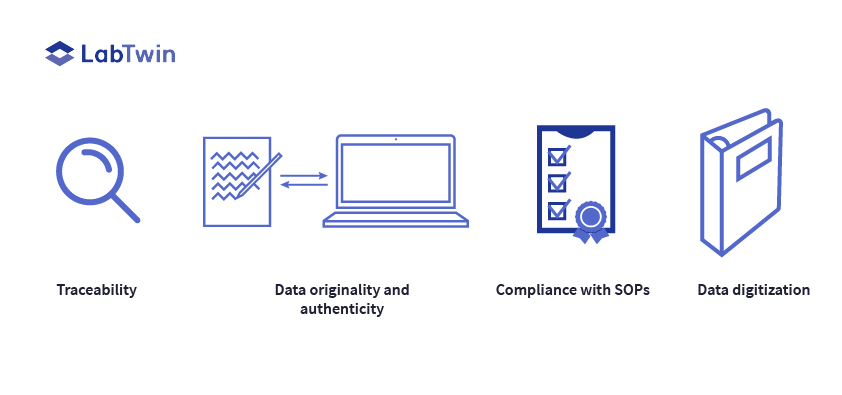
Digital lab assistants are excellent tools for resolving data integrity challenges in GMP environments. Voice assistants are mobile devices that capture manufacturing data and metadata, store voice recordings, give SOP guidance and provide an audit trail.
Eric Cooksey, Principal GMP Auditor at Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc., discusses an example case where the majority of the drug manufacturing process occurs within a biosafety cabinet (BSC). “For each step, the data is required to be contemporaneous, meaning the recording of each activity is required at the same time that it takes place.”
It can be extremely challenging to document activities in clean environments like a BSC without contaminating the product. The standard approach to this situation has required, in the past, a second person to witness the documentation of manufacturing activities and double-check all data entries. A voice-activated digital lab assistant eliminates the need for a second operator, by allowing a technician to capture data simply by speaking.
Gloth says, “LabTwin helps the most when you need to immediately capture data at the place where it’s generated.”
Digital lab assistants also facilitate SOP compliance by automatically digitizing all records when they are created. It is very difficult to measure compliance using paper records. In contrast, digitization helps prove compliance, so SOP inspections run smoothly.
Another major advantage of the digital lab assistant is data traceability during audits. Voice assistants automatically create contemporaneous digital records and track all data use with user identification, electronic signatures and time stamps. These features ensure data integrity and improve the traceability of all records. “What could be better than a system that makes data completely traceable from the reported results all the way back to the creation of the record? I don’t see anything better than that,” says Blasie.
“Protocol adherence often comes up during investigations as root causes for an out-of-specification result. Operators can’t always remember multiple experimental protocol steps for several hours and then write them down accurately after the fact.Sofía Lange
Head of Quality Assurance, Atrium Innovations
“These batches that we’re manufacturing cost a lot of money. If we don’t need a lot of data review or investigations, because everything is digitized, then we can reduce the amount of time that a product is in testing and reduce the cost of manufacturing the batch.”Cheryl Blasie
Director of Analytical Quality & Compliance, Bristol-Myers Squibb
The future of cGMP compliance
In the Lab of the Future, operators will be able to use a digital lab assistant to provide proof of data integrity. They will be able to re-enact the data lifecycle with an inspector with confidence that the inspector will find the data to be accurate and complete.
In the future, digital assistants will also coordinate communication between different laboratory management, quality assurance and inventory systems. This, in turn, will optimize workflows, improve compliance and streamline error management. For example, a fully connected manufacturing facility could automatically flag deviations so staff could deal with them immediately. The end result is significant time and cost savings.
Learn more about how digital lab assistants improve data integrity in this free webinar.